Cloud Computing
Access IT resources and services via the internet with flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency
- Comprehensive Guide

What is Cloud Computing?
In Short
Cloud computing refers to a set of services accessible via the internet that allow users to store and run software, applications, data, and other IT resources on remote servers. Instead of having everything installed on your own computer, you access it online—just like a web app or an online service.
In Detail
Software and Applications
Programs such as office software, project management tools, or development platforms can be hosted and used in the cloud.
Data
Files, databases, and other information can be stored in the cloud and accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
Infrastructure
The cloud also includes servers, networks, and other IT resources needed to run applications and manage data.
Advantages
Greater Flexibility
Access your resources from anywhere, anytime with internet connectivity.
Enhanced Scalability
Scale resources up or down based on your business needs.
Cost Savings
Reduce infrastructure costs compared to using physical servers.
Key Benefits
Cloud computing offers greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings compared to using physical servers.
Types of Cloud
Public Cloud
Accessible to anyone via the internet.
Private Cloud
Dedicated to a specific organization.
Hybrid Cloud
A combination of public and private cloud environments.
Examples of Cloud Services
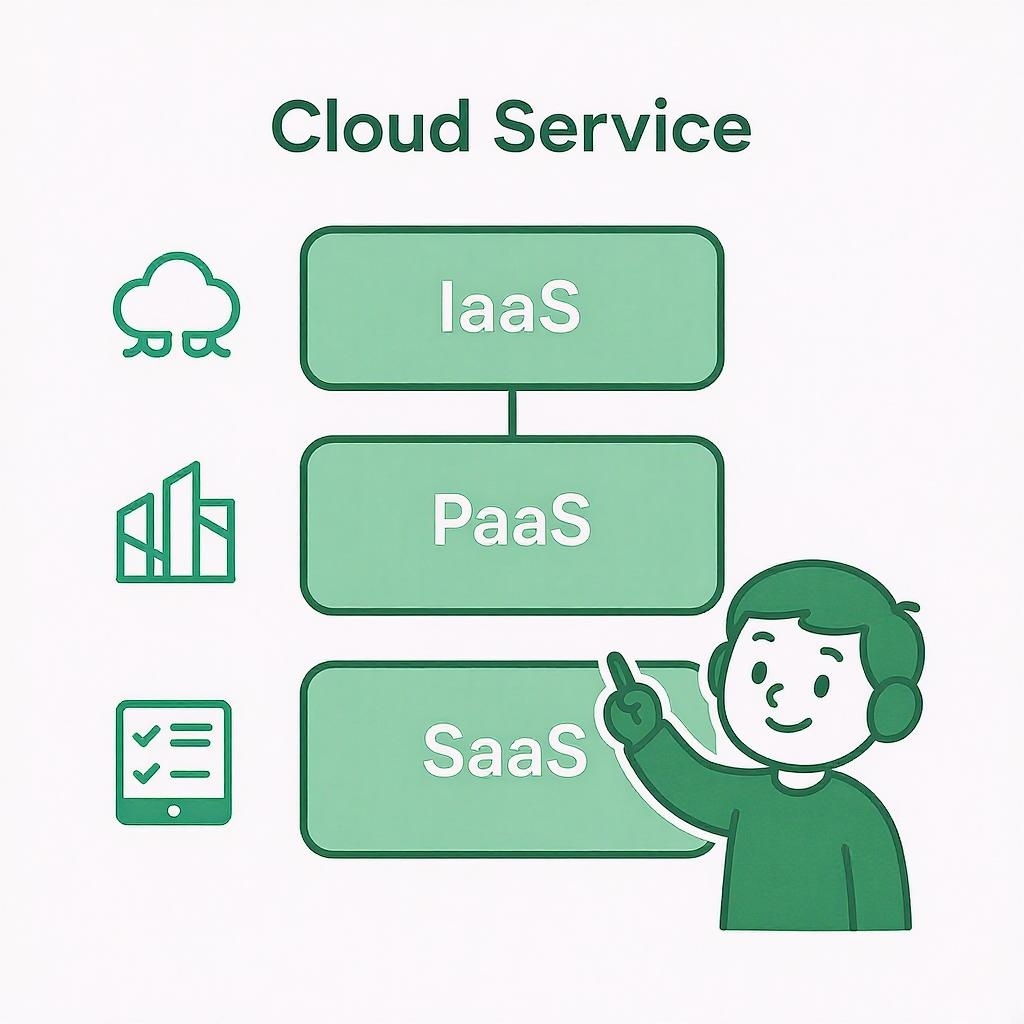
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Provides basic computing resources such as virtual servers, storage systems, and networks.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Offers a platform to develop, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
Delivers software applications directly online, such as office suites or project management tools.
Cloud Gaming
